American Foulbrood, attributable to Paenibacillus larvae, is probably the most extreme bacterial illness of honey bees (Apis mellifera).
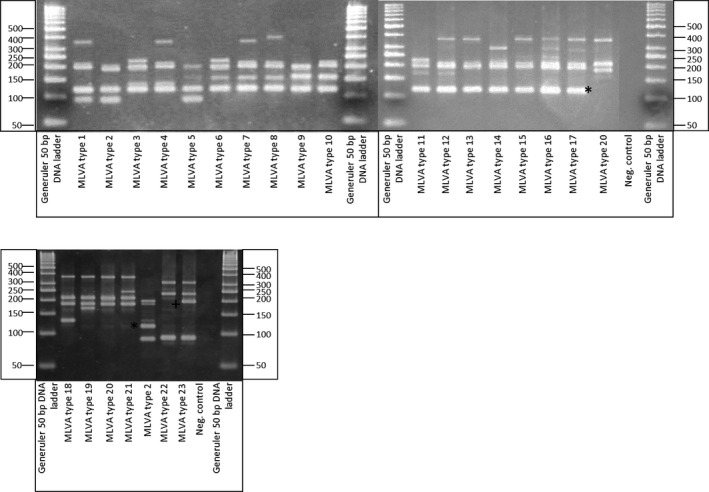
To carry out genotyping of P. larvae in an epidemiological context, there’s a want of a quick and low cost methodology with a excessive decision. Here, we suggest Multiple Locus Variable number of tandem repeat Analysis (MLVA).
MLVA has been used for typing a group of 209 P. larvae strains from which 23 totally different MLVA sorts might be recognized. Moreover, the developed methodology not solely permits the identification of the 4 Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus (ERIC) genotypes, however permits additionally a discriminatory subdivision of probably the most dominant ERIC kind I and ERIC kind II genotypes.
A biogeographical research has been performed exhibiting a big correlation between MLVA genotype and the geographical area the place it was remoted.

Analysis of scientific and environmental Candida parapsilosis isolates by microsatellite genotyping–a tool for hospital an infection surveillance.
Candida parapsilosis emerged as an vital opportunistic pathogen, inflicting candidaemia worldwide. Nosocomial outbreaks triggered by this species have been ceaselessly described, notably in most cancers sufferers.
For a greater understanding of its epidemiology, a number of typing strategies are used and microsatellite evaluation has been reported as extremely discriminant.
The fundamental goal of this work was to review C. parapsilosis isolates by utility of microsatellite genotyping to tell apart epidemiologically associated strains, examine scientific and environmental isolates and decide doable routes of dispersion of the isolates within the hospital setting.
A complete of 129 C. parapsilosis isolates from totally different origins, together with hospital atmosphere and fingers of healthcare staff, had been genotyped utilizing 4 microsatellite markers. The isolates had been recovered from totally different well being establishments.
Analysis of C. parapsilosis isolates from hospital atmosphere confirmed nice genotypic range; nevertheless, the identical or very related genotypes had been additionally discovered.
The identical multilocus genotype was shared by isolates recovered from the hand of a healthcare employee, from the hospital atmosphere and from sufferers of the identical healthcare establishment, suggesting that these might be doable routes of transmission and that infections attributable to C. parapsilosis could also be primarily associated with exogenous transmission to the affected person.
Examination of sequential isolates from the identical sufferers confirmed that colonizing and bloodstream isolates had the identical multilocus genotype within the majority of instances. We reveal that this typing methodology is ready to distinguish clonal clusters from genetically unrelated genotypes and may be a helpful tool to assist epidemiologic investigations within the hospital setting.
